KYC Compliance in Cameroon: 2025 Guide to Digital Identity and AML Regulations
Explore KYC and eKYC regulations shaping Cameroon’s fintech sector in 2025. Learn about AML laws, regulators, challenges, and how VOVE ID streamlines digital onboarding for compliance and trust.

Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance is critical for financial integrity in Cameroon, fueled by the rapid growth of digital payments, fintech innovation, and cross-border transactions. In 2025, KYC extends beyond identity verification to support Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) efforts, financial inclusion, and digital transformation. This guide targets fintechs, banks, and mobile money providers navigating Cameroon’s evolving regulatory landscape.
Adopting electronic KYC (eKYC) solutions like VOVE ID enables businesses to streamline onboarding, reduce fraud, and meet stringent AML obligations efficiently, fostering trust and scalability in Cameroon’s financial ecosystem.
Regulatory Framework: Who Oversees KYC in Cameroon
Cameroon’s KYC and AML framework combines national legislation with regional standards under the Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC). Key regulations and bodies include:
Key Laws and Regulations
- Law No. 2010/012 of 21 December 2010: Mandates financial institutions to verify customer identities, monitor transactions, and report suspicious activities to combat money laundering and terrorism financing.
- COBAC and BEAC Directives: The Banking Commission of Central Africa (COBAC) and the Bank of Central African States (BEAC) enforce harmonized KYC/AML standards across CEMAC.
- Decree on Beneficial Ownership Transparency: Requires disclosure of ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs) to enhance corporate transparency.
- Law No. 2010/013 on Personal Data Protection: Ensures secure handling of customer data during KYC processes, aligning with global privacy standards.
- FATF and GABAC Alignment: Cameroon’s inclusion on FATF’s grey list and GABAC’s 2024 mutual evaluation drive stricter AML/CFT compliance.
Key Institutions
- ANIF (Agence Nationale d’Investigation Financière): Cameroon’s Financial Intelligence Unit, responsible for receiving and analyzing suspicious transaction reports (STRs).
- COBAC: Supervises financial institutions, ensuring robust KYC/AML controls.
- BEAC: Regulates monetary policy and payment systems, enforcing KYC for digital transactions.
- Ministry of Finance: Coordinates financial inclusion policies and AML compliance strategies.
KYC Process in Cameroon
KYC compliance applies to banks, microfinance institutions (MFIs), payment providers, insurance firms, and fintechs. The process involves:
| Step | Requirement | Responsible Entities | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identity Collection | Obtain official ID documents | Banks, Fintechs, Mobile Operators | National ID, passport, or voter card, plus proof of address (e.g., utility bill). |
| Verification | Validate authenticity | Regulated Financial Institutions | Use official databases or biometric systems for verification. |
| Corporate Verification (KYB) | Validate business details | Financial Institutions, Fintechs | Confirm registration, UBOs, and authorized signatories. |
| Risk Profiling | Assign risk levels | Compliance Teams | Apply Customer Due Diligence (CDD) or Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients (e.g., PEPs). |
| Monitoring & Reporting | Track and report suspicious activity | All Reporting Entities | File STRs with ANIF within 48 hours of detection. |
| Record Keeping | Maintain KYC data | Institutions under COBAC supervision | Store data for 10 years, per COBAC and Law No. 2010/012 requirements. |
eKYC solutions, such as VOVE ID, digitize this process, reducing onboarding times from days to minutes while ensuring compliance with ANIF and COBAC standards.
Mobile Money and Fintech: The KYC Opportunity
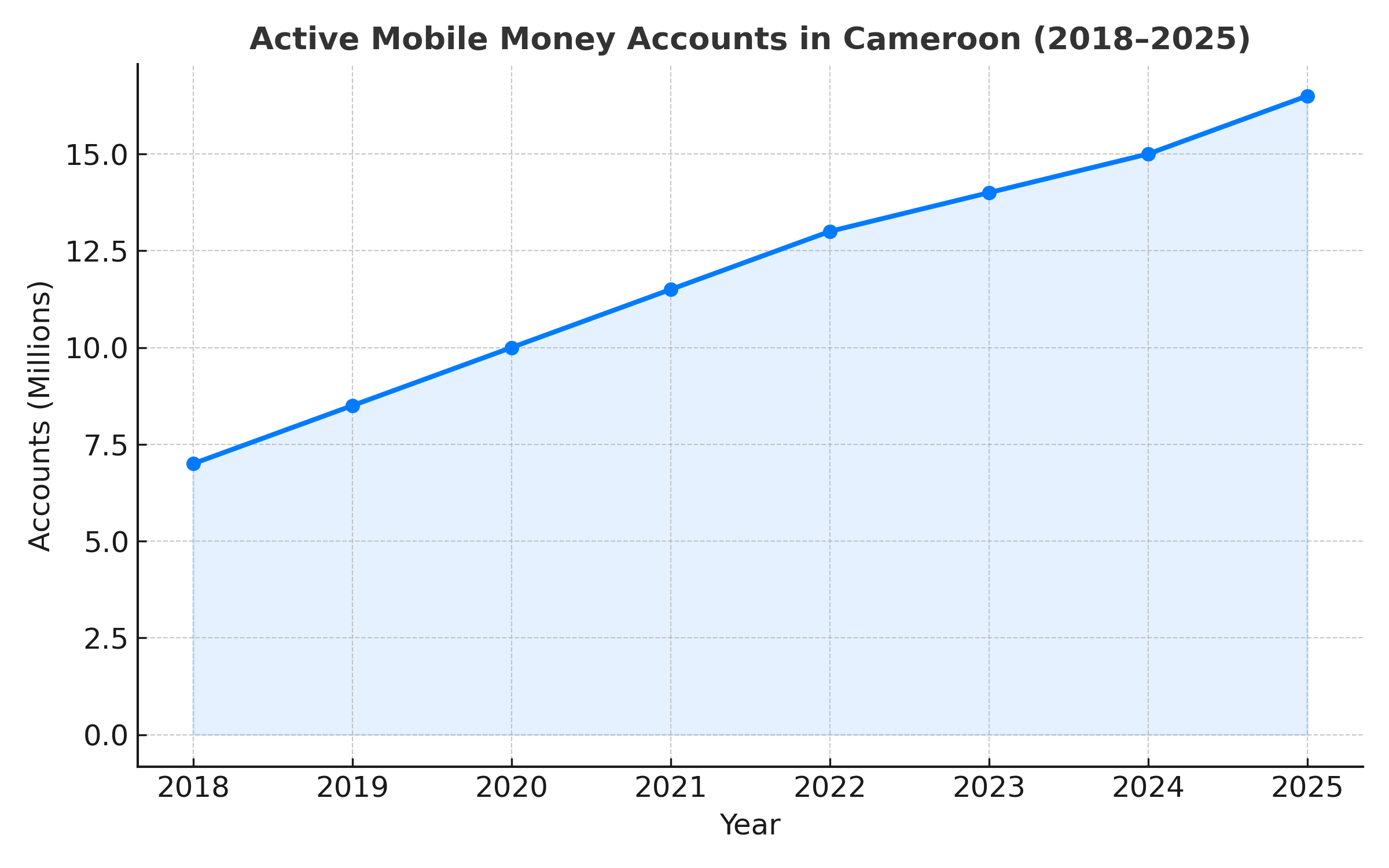
Cameroon’s mobile money market, led by MTN Mobile Money and Orange Money, serves over 15 million active accounts (GSMA, 2024). Tiered KYC frameworks allow basic accounts with minimal verification, but full accounts require comprehensive checks, often slowing onboarding.
Challenges like fragmented ID systems and manual processes exclude rural populations, where ID coverage is below 60% (World Bank, 2024). VOVE ID addresses this by offering:
- Biometric Authentication: Advanced facial recognition and liveness detection prevent fraud and duplicate identities.
- Document Verification: Validates national IDs, passports, and driver’s licenses in real time through secure AI models.
- Scalable Compliance: Aligns with BEAC, COBAC, and FATF standards to support financial inclusion and regulatory trust.Mobile Money Growth in Cameroon
To illustrate the rise of mobile money, the chart below shows the growth of active accounts from 2018 to 2025 (projected).
Challenges in Implementing KYC
Cameroon faces several barriers to seamless KYC compliance:
- Limited ID Penetration: Over 40% of rural Cameroonians lack official IDs (World Bank, 2024), hindering onboarding for fintechs and mobile money providers.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Unreliable internet in rural areas (affecting 30% of the population, per ITU 2024) limits online eKYC adoption.
- Manual Processes: Small MFIs and banks rely on paper-based KYC, increasing errors and onboarding costs by up to 20% (industry estimates).
- Data Security Risks: Inconsistent compliance with the 2010 Data Protection Law raises privacy concerns, with 15% of fintechs reporting breaches in 2024 (ANIF).
- High Compliance Costs: Small fintechs spend 10–15% of revenue on KYC/AML compliance, straining resources (African Fintech Network, 2024).
- Cross-Border Pressure: FATF’s grey-list status requires alignment with global AML standards, increasing scrutiny and costs.
The Future of KYC and Digital Identity in Cameroon
Cameroon’s national digital ID project, set for 2025, will introduce biometric-enabled IDs and interoperable registries, boosting eKYC adoption. This aligns with GABAC’s push for regional AML/CFT harmonization and FATF compliance.
VOVE ID supports this transition by offering:
- Instant Verification: Real-time document and biometric checks via secure APIs and SDKs.
- Fraud Reduction: Liveness detection and biometric verification reduce identity fraud risk.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation and digital onboarding help lower costs compared to fully manual KYC workflows.
- Regulatory Support: Designed to align with global AML/CTF best practices; works to support compliance with Cameroon’s regulatory framework including ANIF, COBAC, and regional/global standards.
Cameroon’s 2024 GABAC evaluation praised its AML progress but urged faster eKYC adoption to close gaps in rural financial inclusion.
Conclusion
Cameroon’s KYC and AML landscape is evolving toward digital trust, transparency, and inclusion. Despite challenges like limited ID coverage and infrastructure gaps, innovations like VOVE ID and the 2025 national digital ID project position fintechs and financial institutions for success. By embracing eKYC, businesses can ensure compliance, reduce costs, and drive inclusive growth in Cameroon’s financial ecosystem in 2025 and beyond. Explore solutions like VOVE ID to stay ahead of regulatory demands.
Empower your compliance journey in Cameroon with VOVE ID.
Start verifying customers instantly, securely, and in full alignment with ANIF and FATF standards.




